Their study, published online by the journal Nano Letters, is the first to demonstrate the use of nanodiamonds, a new class of nanomaterials, in biomedicine. In addition to delivering cancer drugs, the model could be used for other applications, such as fighting tuberculosis or viral infections, say the researchers.
Nanodiamonds promise to play a significant role in improving cancer treatment by limiting uncontrolled exposure of toxic drugs to the body. The research team reports that aggregated clusters of nanodiamonds were shown to be ideal for carrying a chemotherapy drug and shielding it from normal cells so as not to kill them, releasing the drug slowly only after it reached its cellular target.
To make the material effective, Ho and his colleagues manipulated single nanodiamonds, each only two nanometers in diameter, to form aggregated clusters of nanodiamonds, ranging from 50 to 100 nanometers in diameter. The drug, loaded onto the surface of the individual diamonds, is not active when the nanodiamonds are aggregated; it only becomes active when the cluster reaches its target, breaks apart and slowly releases the drug. (With a diameter of two to eight nanometers, hundreds of thousands of diamonds could fit onto the head of a pin.)
“The nanodiamond cluster provides a powerful release in a localized place -- an effective but less toxic delivery method,” said co-author Eric Pierstorff, a molecular biologist and post-doctoral fellow in Ho’s research group. Because of the large amount of available surface area, the clusters can carry a large amount of drug, nearly five times the amount of drug carried by conventional materials.
Liposomes and polymersomes, both spherical nanoparticles, currently are used for drug delivery. While effective, they are essentially hollow spheres loaded with an active drug ready to kill any cells, even healthy cells that are encountered as they travel to their target. Liposomes and polymersomes also are very large, about 100 times the size of nanodiamonds -- SUVs compared to the nimble nanodiamond clusters that can circulate throughout the body and penetrate cell membranes more easily.
Unlike many of the emerging nanoparticles, nanodiamonds are soluble in water, making them clinically important. “Five years ago while working in Japan, I first encountered nanodiamonds and saw it was a very soluble material,” said materials scientist Houjin Huang, lead author of the paper and also a post-doctoral fellow in Ho’s group. “I thought nanodiamonds might be useful in electronics, but I didn’t find any applications. Then I moved to Northwestern to join Dean and his team because they are capable of engineering a broad range of devices and materials that interface well with biological tissue. Here I’ve focused on using nanodiamonds for biomedical applications, where we’ve found success.
“Nanodiamonds are very special,” said Huang. “They are extremely stable, and you can do a lot of chemistry on the surface, to further functionalize them for targeting purposes. In addition to functionality, they also offer safety -- the first priority to consider for clinical purposes. It’s very rare to have a nanomaterial that offers both.”
“It’s about optimizing the advantages of a material,” said Ho, a member of the Lurie Cancer Center. “Our team was the first to forge this area -- applying nanodiamonds to drug delivery. We’ve talked to a lot of clinicians and described nanodiamonds and what they can do. I ask, ‘Is that useful to you?’ They reply, ‘Yes, by all means.’”
For their study, Ho and his team used living murine macrophage cells, human colorectal carcinoma cells and doxorubicin hydrochloride, a widely used chemotherapy drug. The drug was successfully loaded onto the nanodiamond clusters, which efficiently ferried the drug inside the cells. Once inside, the clusters broke up and slowly released the drug.
In the genetic studies, the researchers exposed cells to the bare nanodiamonds (no drug was present) and analyzed three genes associated with inflammation and one gene for apoptosis, or cell death, to see how the cells reacted to the foreign material. Looking into the circuitry of the cell, they found no toxicity or inflammation long term and a lack of cell death. In fact, the cells grew well in the presence of the nanodiamond material.
support this site
Showing posts with label nanomedicine. Show all posts
Showing posts with label nanomedicine. Show all posts
Friday, October 12, 2007
Nanodiamonds delivery chemotherapy drugs without negative side effects
Northwestern University researchers have shown that nanodiamonds -- much like the carbon structure as that of a sparkling 14 karat diamond but on a much smaller scale -- are very effective at delivering chemotherapy drugs to cells without the negative effects associated with current drug delivery agents.
Thursday, September 20, 2007
Introduction to nanopharmaceuticals
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology. It covers areas such as nanoparticle drug delivery and possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology (MNT) and nanovaccinology.
A definition from the Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences of Great Britain.
The European Science Foundation definition.
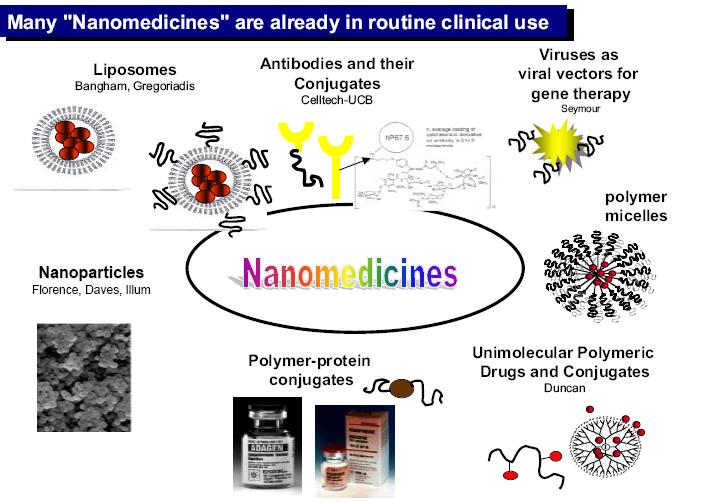
Nanopharmaceuticals as a big part of what nanomedicine is today. From the Ruth Duncan presentation.
Various kinds of nanoscale particles used for nanopharmaceuticals
Nanoparticles is a microscopic particle with at least one dimension less than 100 nm.
Liposomes is a spherical vesicle composed of a bilayer membrane. In biology, this specifically refers to a membrane composed of a phospholipid and cholesterol bilayer
Antibody conjugates
A conjugate vaccine is created by covalently attaching a poor antigen to a carrier protein, thereby conferring the immunological attributes of the carrier on the attached antigen. This technique for the creation of an effective immunogen is most often applied to bacterial polysaccharides for the prevention of invasive bacterial disease.
polymer therapeutics
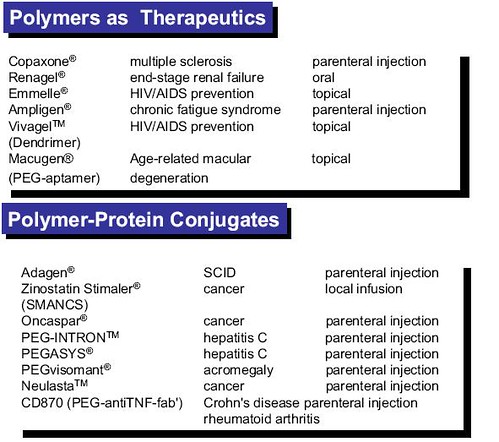
From the Ruth Duncan presentation
Buckyballs and Nanotubes
Nanoemulsions is a type of emulsion in which the sizes of the particles in the dispersed phase are defined as less than 1000 nanometers. A nanoemulsion of soybean oil to create drops of 400-600 nanometers in diameter will kill many pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
Dendrimers - Dendrimers are synthetic polymers, a thousand times smaller than cells. Dendrimers can be synthesized in various predetermined sizes, and can interact with biological agents by modifying their surface properties.
FURTHER READING
An article on nanopharmaceuticals and veterinary medicine
Presentation by Ruth Duncan on nanopharmaceuticals
A nanopharmaceuticals site
A definition from the Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences of Great Britain.
Nanopharmaceuticals represent an emerging field where the nanoscale element may refer to either the size of the drug particle or to a therapeutic delivery system. These therapeutic systems may be defined as a complex system consisting of at least two components, one of which is the active ingredient. In this field the concept of nanoscale is the range from 1 to 1,000nm. The definition includes polymer therapeutics, which share many characteristics with macromolecular prodrugs such as antibody conjugates of drugs.
The European Science Foundation definition.
Nanopharmaceuticals can be developed either as drug delivery systems or biologically active drug products.
This sub-discipline is defined as the science and technology of nanometre size scale complex systems, consisting of at least two components, one of which being the active ingredient. In this field the concept of nanoscale was seen to range from 1 to 1000 nm.

Nanopharmaceuticals as a big part of what nanomedicine is today. From the Ruth Duncan presentation.
Various kinds of nanoscale particles used for nanopharmaceuticals
Nanoparticles is a microscopic particle with at least one dimension less than 100 nm.
Liposomes is a spherical vesicle composed of a bilayer membrane. In biology, this specifically refers to a membrane composed of a phospholipid and cholesterol bilayer
Antibody conjugates
A conjugate vaccine is created by covalently attaching a poor antigen to a carrier protein, thereby conferring the immunological attributes of the carrier on the attached antigen. This technique for the creation of an effective immunogen is most often applied to bacterial polysaccharides for the prevention of invasive bacterial disease.
polymer therapeutics

From the Ruth Duncan presentation
Buckyballs and Nanotubes
Nanoemulsions is a type of emulsion in which the sizes of the particles in the dispersed phase are defined as less than 1000 nanometers. A nanoemulsion of soybean oil to create drops of 400-600 nanometers in diameter will kill many pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
Quantum Dots is a semiconductor nanostructure that confines the motion of conduction band electrons, valence band holes, or excitons (bound pairs of conduction band electrons and valence band holes) in all three spatial directions. The confinement can be due to electrostatic potentials (generated by external electrodes, doping, strain, impurities), the presence of an interface between different semiconductor materials (e.g. in core-shell nanocrystal systems), the presence of the semiconductor surface (e.g. semiconductor nanocrystal), or a combination of these
Small quantum dots, such as colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals, can be as small as 2 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to 10 to 50 atoms in diameter and a total of 100 to 100,000 atoms within the quantum dot volume. Self-assembled quantum dots are typically between 10 and 50 nm in size. Quantum dots defined by lithographically patterned gate electrodes, or by etching on two-dimensional electron gases in semiconductor heterostructures can have lateral dimensions exceeding 100 nm. At 10 nm in diameter, nearly 3 million quantum dots could be lined up end to end and fit within the width of a human thumb.
Dendrimers - Dendrimers are synthetic polymers, a thousand times smaller than cells. Dendrimers can be synthesized in various predetermined sizes, and can interact with biological agents by modifying their surface properties.
FURTHER READING
An article on nanopharmaceuticals and veterinary medicine
Presentation by Ruth Duncan on nanopharmaceuticals
A nanopharmaceuticals site
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)